 How CSRA Builds Trust at Scale shares some of the most surprising and useful things I’ve learned while pioneering experiential social media since 2006. In this post, I’ll reveal how experiential social media teams build trust by breaking some rules in social media. How CSRA Builds Trust at Scale shares some of the most surprising and useful things I’ve learned while pioneering experiential social media since 2006. In this post, I’ll reveal how experiential social media teams build trust by breaking some rules in social media.
If you’d like to watch this post instead of reading it, click the thumbnail button!
[…]
 Three Powerful Experiential Social Media Lessons shares three surprising breakthrough insights I’ve learned while practicing experiential social media. This is one of the videos I’ve made to share some of the most useful things I’ve learned since 2006. Three Powerful Experiential Social Media Lessons shares three surprising breakthrough insights I’ve learned while practicing experiential social media. This is one of the videos I’ve made to share some of the most useful things I’ve learned since 2006.
If you’d like to watch this post instead of reading it, click the thumbnail button!
[…]
 In Healing Business, I’ll share why I think business needs healing and how CSRA is doing it with experiential social media. Business is wounded from a human point of view because it’s become very impersonal; large organizations don’t mean to, but they treat employees and customers as numbers because they don’t know or trust them. Experiential is a practical way to change that. In Healing Business, I’ll share why I think business needs healing and how CSRA is doing it with experiential social media. Business is wounded from a human point of view because it’s become very impersonal; large organizations don’t mean to, but they treat employees and customers as numbers because they don’t know or trust them. Experiential is a practical way to change that.
If you’d like to watch this post instead of reading it, click the thumbnail button!
[…]
 11 Celebration summarizes my reflections on CSRA’s first decade in business, and my vision for our next decade. We’ve been pioneering in experiential social media and social business transformation since I founded the firm in February 2006. 11 Celebration summarizes my reflections on CSRA’s first decade in business, and my vision for our next decade. We’ve been pioneering in experiential social media and social business transformation since I founded the firm in February 2006.
It’s difficult to encapsulate ten years of learnings, but that hasn’t stopped me from trying! This page will reprise some of my favorite posts, and it will feature a series of videos I’ve made in which I explain where we’ve been and where we’re going. This post will change frequently, so please consider it a work in progress.
[…]
 On human experience invites you to examine common marketing practices from a human experience perspective. It expands part of a presentation I gave at the University of Chicago Booth that the audience experienced as mind-bending based on their facial expressions. On human experience invites you to examine common marketing practices from a human experience perspective. It expands part of a presentation I gave at the University of Chicago Booth that the audience experienced as mind-bending based on their facial expressions.
Quite by accident I’ve happened on a rare view of humanity while practicing experiential social media during the last ten years. Experiential’s core research process involves conducting ethnographic research of thousands of people in specific situations. I analyze human behavior in communities in digital public, and it’s very rich, nuanced and complex. Ethnographic yields unparalleled qualitative and quantitative insights into behavior and human experience.
Experiential consistently reveals that many marketing practices repel people rather than attracting them because the environment in which marketing is practiced has completely changed from when these practices developed. Marketing creates mistrust and pushes people away, as I’ll show below. This post attempts to reveal this anachronism to you, so you can correct your practices and take the advantage from your competitors.
[…]
 [Updated] Many businesses live in fear, and how to break free reveals how fear and risk can be sharply reduced by increasing trust among employees, customers and partners. [Updated] Many businesses live in fear, and how to break free reveals how fear and risk can be sharply reduced by increasing trust among employees, customers and partners.
I have learned many surprising things while practicing experiential social media, but one of the most astounding is the realization that most business practices, especially those that concern people, are grounded in fear and mistrust. This ties businesses in knots, but few people realize it because it’s accepted as normal. This post aims to open your eyes, so you can start noticing how fear and mistrust operate in your firm. Then I’ll offer numerous ideas that can help you to reduce fear and risk by increasing trust.
[…]
 Ethnographic research for design explains how to use advances in ethnographic research of social media to design products, services, experiences… anything—while getting better results at lower risk. Ethnographic research of social media is breakthrough for designers in the “design stack” in which I’ve includedArchitecture/Interior Design, Product Design, User Experience Design/Interaction Design, UX Strategy, Service Design and Customer Experience Design. Ethnographic research for design explains how to use advances in ethnographic research of social media to design products, services, experiences… anything—while getting better results at lower risk. Ethnographic research of social media is breakthrough for designers in the “design stack” in which I’ve includedArchitecture/Interior Design, Product Design, User Experience Design/Interaction Design, UX Strategy, Service Design and Customer Experience Design.
Designers in all fields lament clients’ resistance to funding robust research. Traditional design research methods are often grounded in asking proposed users explicit questions, and self-reported responses vary significantly from actual behavior despite respondents’ best intentions. Similarly, shadowing, service safaris, “a day in the life,” and other analog research methods are costly and slow. Sample sizes are necessarily small because scaling analog methods greatly multiplies the budget and length of the research phase. Ethnographic research of social media changes the game because it studies proposed users’ actual behavior in digital public when they’re having heated discussions about the outcomes they want when the proposed product, service, or process is useful to them. It […]
 Behavioral economics autonomy and ethics is a thought experiment on how to approach “doing good” when applying the emerging practice of behavioral economics. Along with big data analytics and cognitive science, behavioral economics affords businesses, governments and other organizations unprecedented impact on individuals’ behavior, even without their consent or awareness. This arouses serious ethical and social dilemmas. Behavioral economics autonomy and ethics is a thought experiment on how to approach “doing good” when applying the emerging practice of behavioral economics. Along with big data analytics and cognitive science, behavioral economics affords businesses, governments and other organizations unprecedented impact on individuals’ behavior, even without their consent or awareness. This arouses serious ethical and social dilemmas.
Every behavioral economics practitioner I’ve met has emphasized the importance of using its practice “for good” in order to help people. Like all other human endeavors, however, “for good” is open to interpretation, so I’ll apply my experience with ethnographic and behavioral analysis of social media to reflect on what “for good” might mean in light of individual and group autonomy.
I also hope this Noodle will be food for thought for executives who hire behavioral economics firms as well as all of us who are invariably its subject. In a similar vein, most designers I know are committed to using design principles to improve user experience, and there’s considerable overlap between design and behavioral economics.
Behavioral economics is […]
 Ethnographic research for business innovation shows how to apply ethnographic research of social media to managing controlled disruption within organizations. Ethnographic research of social media can transform the entire innovation process because it’s a very efficient way to study the behavior and motivations of the people that the innovation proposes to serve. Unlike traditional innovation and ethnographic research methods, which are relatively slow, costly and qualitative, ethnographic research of social media combines qualitative richness with quantitative analysis. It’s faster and less costly, too. Ethnographic research for business innovation shows how to apply ethnographic research of social media to managing controlled disruption within organizations. Ethnographic research of social media can transform the entire innovation process because it’s a very efficient way to study the behavior and motivations of the people that the innovation proposes to serve. Unlike traditional innovation and ethnographic research methods, which are relatively slow, costly and qualitative, ethnographic research of social media combines qualitative richness with quantitative analysis. It’s faster and less costly, too.
Ethnographic research for business innovation can dramatically improve the depth and breadth of business and corporate strategy, business design and service design research since it allows teams to consider more users and to assess their behavior and motivations, which can improve the value of more costly research.
This post outlines the business innovation use case of ethnographic research of social media, and it includes examples in banking, professional services, consumer products, and B2B marketing. For more on ethnographic research, see More Resources below.
[…]
Social media strategy lessons learned summarizes eleven golden rules I’ve learned while leading strategy and its execution for global firms. Some of them might surprise you: I’ve come to learn that I have a different perspective on social media strategy since I advised global firms and startups in their corporate strategies before founding CSRA in 2006.
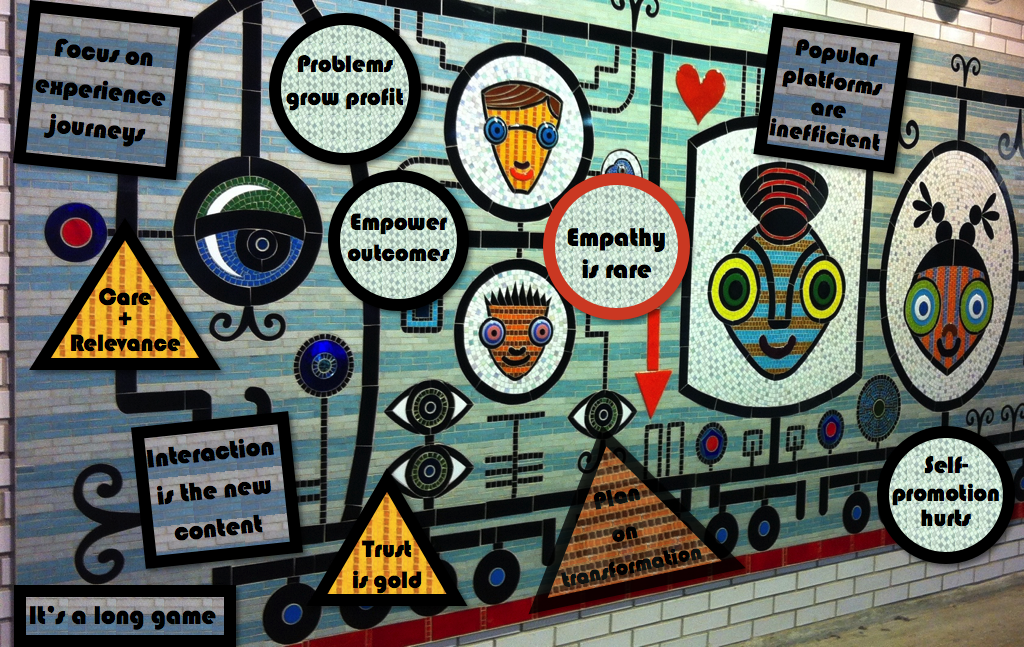
Before diving into lessons learned, let’s specify what we mean by social media strategy. “Strategy” itself is an overused work that denotes some mixture of research and planning. The strategy trade-off is simple: the more research and analysis you do upfront, the more risks you can foresee and account for in your plan. When you put your plan into action, you make fewer mistakes and execute more efficiently. Conversely, “minimum viable”/lean strategy does less research upfront, so the team learns while doing. Neither approach is universally “right,” and both work best for certain situations and firms.
[…]
|
|
 How CSRA Builds Trust at Scale shares some of the most surprising and useful things I’ve learned while pioneering experiential social media since 2006. In this post, I’ll reveal how experiential social media teams build trust by breaking some rules in social media.
How CSRA Builds Trust at Scale shares some of the most surprising and useful things I’ve learned while pioneering experiential social media since 2006. In this post, I’ll reveal how experiential social media teams build trust by breaking some rules in social media.
 Three Powerful Experiential Social Media Lessons shares three surprising breakthrough insights I’ve learned while practicing experiential social media. This is one of the videos I’ve made to share some of the most useful things I’ve learned since 2006.
Three Powerful Experiential Social Media Lessons shares three surprising breakthrough insights I’ve learned while practicing experiential social media. This is one of the videos I’ve made to share some of the most useful things I’ve learned since 2006. In Healing Business, I’ll share why I think business needs healing and how CSRA is doing it with experiential social media. Business is wounded from a human point of view because it’s become very impersonal; large organizations don’t mean to, but they treat employees and customers as numbers because they don’t know or trust them. Experiential is a practical way to change that.
In Healing Business, I’ll share why I think business needs healing and how CSRA is doing it with experiential social media. Business is wounded from a human point of view because it’s become very impersonal; large organizations don’t mean to, but they treat employees and customers as numbers because they don’t know or trust them. Experiential is a practical way to change that. 11 Celebration summarizes my reflections on CSRA’s first decade in business, and my vision for our next decade. We’ve been pioneering in experiential social media and social business transformation since I founded the firm in February 2006.
11 Celebration summarizes my reflections on CSRA’s first decade in business, and my vision for our next decade. We’ve been pioneering in experiential social media and social business transformation since I founded the firm in February 2006. On human experience invites you to examine common marketing practices from a human experience perspective. It expands part of a presentation I gave at the University of Chicago Booth that the audience experienced as mind-bending based on their facial expressions.
On human experience invites you to examine common marketing practices from a human experience perspective. It expands part of a presentation I gave at the University of Chicago Booth that the audience experienced as mind-bending based on their facial expressions. [Updated] Many businesses live in fear, and how to break free reveals how fear and risk can be sharply reduced by increasing trust among employees, customers and partners.
[Updated] Many businesses live in fear, and how to break free reveals how fear and risk can be sharply reduced by increasing trust among employees, customers and partners. Ethnographic research for design explains how to use advances in ethnographic research of social media to design products, services, experiences… anything—while getting better results at lower risk. Ethnographic research of social media is breakthrough for designers in the “design stack” in which I’ve includedArchitecture/Interior Design, Product Design, User Experience Design/Interaction Design, UX Strategy, Service Design and Customer Experience Design.
Ethnographic research for design explains how to use advances in ethnographic research of social media to design products, services, experiences… anything—while getting better results at lower risk. Ethnographic research of social media is breakthrough for designers in the “design stack” in which I’ve includedArchitecture/Interior Design, Product Design, User Experience Design/Interaction Design, UX Strategy, Service Design and Customer Experience Design. Behavioral economics autonomy and ethics is a thought experiment on how to approach “doing good” when applying the emerging practice of behavioral economics. Along with big data analytics and cognitive science, behavioral economics affords businesses, governments and other organizations unprecedented impact on individuals’ behavior, even without their consent or awareness. This arouses serious ethical and social dilemmas.
Behavioral economics autonomy and ethics is a thought experiment on how to approach “doing good” when applying the emerging practice of behavioral economics. Along with big data analytics and cognitive science, behavioral economics affords businesses, governments and other organizations unprecedented impact on individuals’ behavior, even without their consent or awareness. This arouses serious ethical and social dilemmas. Ethnographic research for business innovation shows how to apply ethnographic research of social media to managing controlled disruption within organizations. Ethnographic research of social media can transform the entire innovation process because it’s a very efficient way to study the behavior and motivations of the people that the innovation proposes to serve. Unlike traditional innovation and ethnographic research methods, which are relatively slow, costly and qualitative, ethnographic research of social media combines qualitative richness with quantitative analysis. It’s faster and less costly, too.
Ethnographic research for business innovation shows how to apply ethnographic research of social media to managing controlled disruption within organizations. Ethnographic research of social media can transform the entire innovation process because it’s a very efficient way to study the behavior and motivations of the people that the innovation proposes to serve. Unlike traditional innovation and ethnographic research methods, which are relatively slow, costly and qualitative, ethnographic research of social media combines qualitative richness with quantitative analysis. It’s faster and less costly, too.